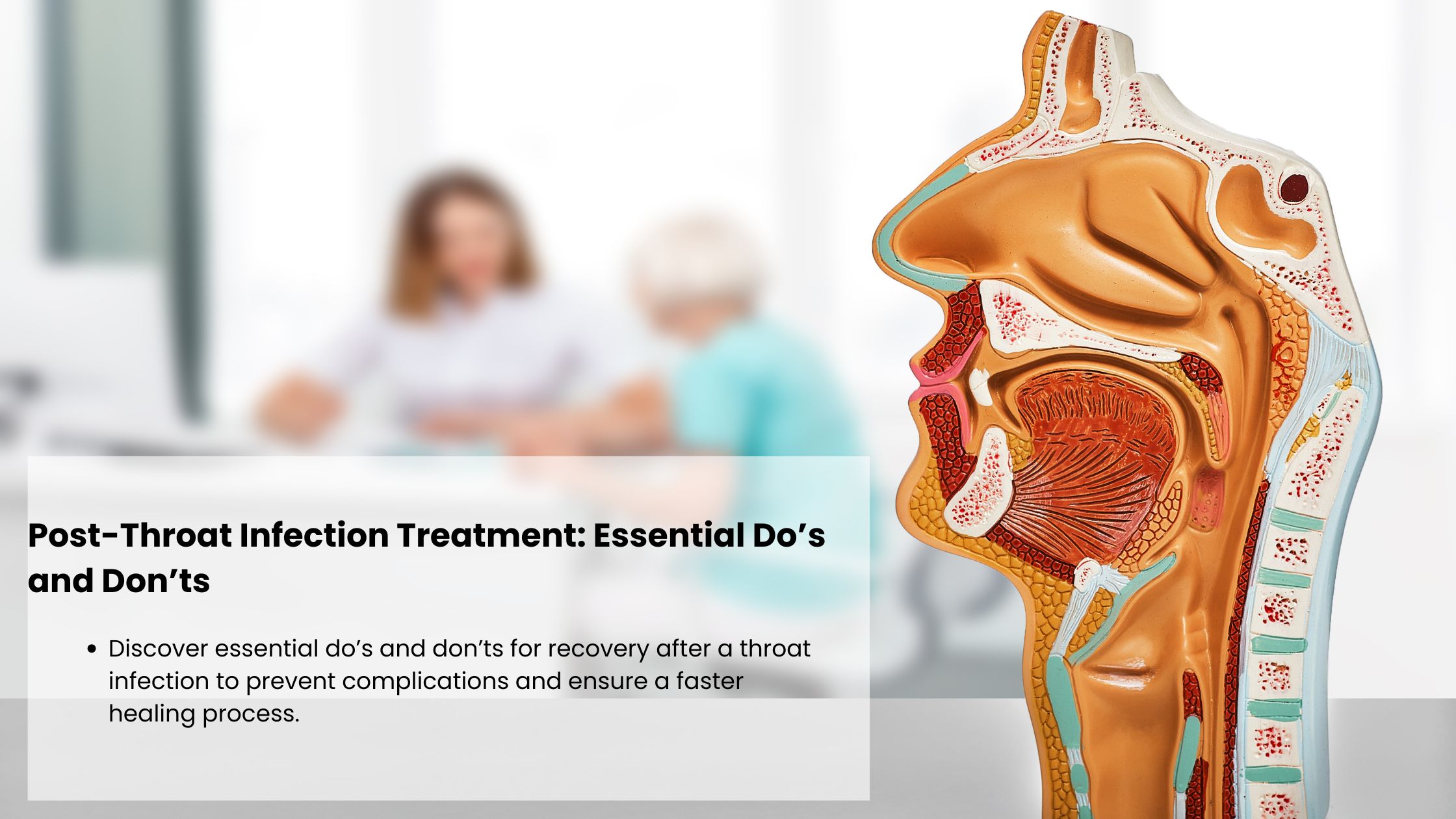
A perceived ringing, buzzing, hissing, whistling, or other sound in the ears when there is no external sound is known medically as tinnitus. Although frustrating, 15-20% of people are said to be affected by this illness, which is very prevalent. As a sign of an underlying medical issue such as hearing loss, a circulatory system disorder, or damage to the auditory system, tinnitus is not a disease in and of itself. The continual phantom sounds can have a serious negative influence on the quality of life by making it difficult to sleep, anxious, depressed, and concentrate. Each person’s experience with tinnitus is unique, and it might affect one or both ears. Those seeking relief from this auditory disorder should be aware of the possible causes, risk factors, and available treatments. Many people with tinnitus can lessen their symptoms with the right diagnosis and care.
Signs and Symptoms of Tinnitus
- The primary indicator of tinnitus is the continuous presence of phantom noises in the ears. These noises can take the form of ringing, buzzing, hissing, whistling, clicking, or whirring. Some individuals perceive it as a high-pitched screech or a low rumble. The noises may be consistent, sporadic, constant, or intermittent. Tinnitus can manifest in one ear or both ears simultaneously. For many people, the volume and characteristics of the noise change over time.ā
- Although tinnitus itself is not physically painful, the persistent noise can be highly irritating and disruptive. It can hinder one’s ability to focus by overpowering real external sounds. The noises are often most noticeable and troublesome in quiet settings, such as when trying to sleep, which can worsen insomnia. The ceaseless noise can also lead to feelings of anxiety, stress, and depression in individuals with tinnitus, further diminishing their quality of life.
What causes tinnitus?
A. Common Causes
- Age-related hearing loss: The natural process of ageing can result in age-related hearing loss, which often manifests as a form of tinnitus.
- Exposure to loud noises: Prolonged exposure to loud noises, such as attending concerts or working with heavy machinery, can harm the delicate structures within the inner ear and contribute to tinnitus.
- Earwax buildup: Tinnitus can be caused by the accumulation of earwax, which can obstruct the ear canal and impede normal hearing.
- Ear infections: Infections affecting the ear canal or middle ear can serve as a trigger for tinnitus symptoms.
B. Less Common Causes
- Ménière’s disease: Ménière’s disease is a condition that affects the inner ear and can result in episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus.
- Jaw joint problems (TMJ): Temporomandibular joint dysfunction, also known as TMJ, can cause tinnitus along with other symptoms.
- Head and neck tumors: tumors in the head or neck area can put pressure on the auditory nerves, leading to tinnitus.
- Certain medications: Tinnitus can also be caused or worsened by certain medications, including antibiotics, antidepressants, and high doses of aspirin.

How is tinnitus diagnosed?
- There is not a single test available to definitively diagnose tinnitus, as it is not a disease itself but rather a symptom of an underlying condition. When you go to see an ENT doctor or audiologist for tinnitus evaluation, they will begin by inquiring about your medical history and gathering information about the sounds you are experiencing. They will likely conduct a physical examination of your ears and administer a comprehensive hearing test to assess any potential hearing loss.
- Additional tests such as a CT or MRI scan may be requested to identify any abnormalities or tumors that could be contributing to the tinnitus. Obtaining an accurate diagnosis is crucial to properly address any underlying medical conditions that may be causing the ringing, buzzing, or other phantom sounds.
Treatment and Medication Options for Tinnitus
A. Management Techniques (for most cases)
- Sound therapy: Sound therapy involves the utilization of external sounds, such as white noise or nature sounds, to conceal the presence of tinnitus and reduce its perceptibility.
- Hearing aids: Hearing aids are designed to amplify external sounds, which can divert attention from the internal noise caused by tinnitus and enhance overall hearing abilities.
- Relaxation techniques: To alleviate tinnitus symptoms, relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can be employed to effectively manage stress, as stress tends to worsen the symptoms associated with tinnitus.
B. Treatment for Underlying Conditions (if applicable)
- Earwax removal: Excess earwax can be cleared from the ear canal to relieve tinnitus symptoms caused by blockage.
- Treating ear infections: To address ear infections and the accompanying tinnitus, healthcare professionals may prescribe antibiotics or other medications.
- Medication adjustments: Tinnitus symptoms caused by specific medications can be reduced or eliminated by making adjustments to the medication regimen, such as switching to alternative drugs or modifying dosages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tinnitus, which presents as ringing, buzzing, or clicking noises in the ears, impacts a considerable number of people. It may result from different factors such as age-related hearing decline or exposure to loud sounds, underscoring the importance of seeking expert assistance for precise diagnosis and tailored treatment. Those dealing with tinnitus are encouraged to promptly seek guidance from an otolaryngologist such as a skilled ENT specialist, Dr. Sushant Joshi for a comprehensive assessment and effective management techniques.
At the top ENT facility in Udaipur, Dr Sushant Joshi can offer a precise diagnosis and tailored treatment choices for your issue.
By familiarising themselves with the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment choices for tinnitus, individuals can proactively work towards enhancing their overall well-being.
Also read – Bug in Ear: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments