1. The Truth About Ear Wax
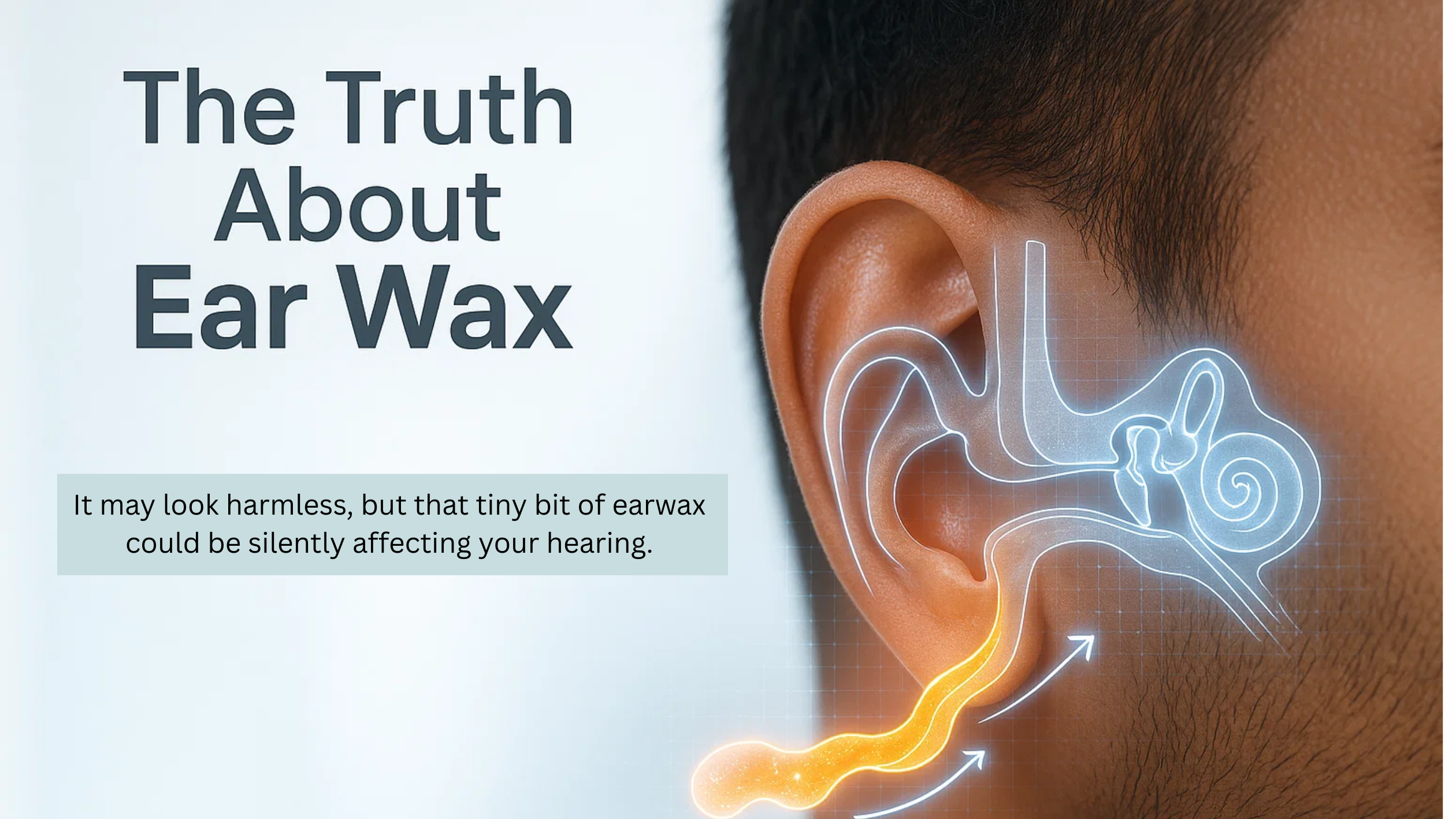
Most of us don’t think twice about earwax until it starts blocking our hearing or causing irritation. At first glance, it seems harmless—just a bit of sticky substance that doesn’t need much attention. But here’s the reality: ignoring earwax can lead to bigger ear health problems.
Earwax, also called cerumen, plays an important role in keeping your ears clean and protected. However, when it builds up excessively or is removed incorrectly, it can cause pain, infection, or even hearing loss.
2. What Exactly Is Ear Wax?
Earwax isn’t just “dirt” in your ears—it’s a natural mix of oil, sweat, dead skin cells, and trapped dust. It protects the ear by keeping it clean, lubricated, and reducing the risk of infections. While a small amount is healthy, too much buildup can cause discomfort or hearing problems.
Functions of Ear Wax:
- Protection: Forms a natural barrier against bacteria, fungi, and foreign objects.
- Lubrication: Prevents dryness and itching inside the ear canal.
- Cleaning Mechanism: Gradually moves outward, carrying dirt and dead skin cells with it.
In short, earwax is nature’s way of keeping your ears safe and healthy.
3. Common Myths About Ear Wax
Earwax is often misunderstood, leading to unnecessary worry or improper cleaning habits. Knowing the facts helps you protect your ears while avoiding common mistakes that can cause discomfort or infections.
- Myth 1: “Earwax means poor hygiene.”
False. Earwax is not dirt—it’s a natural secretion your body produces for protection. - Myth 2: “You should clean your ears daily.”
False. Overcleaning strips your ears of protective wax, leading to irritation and infection. - Myth 3: “Cotton swabs are safe to use.”
False. They actually push wax deeper into the canal, creating blockages.
4. When Ear Wax Becomes a Problem
Sometimes, earwax doesn’t come out naturally and builds up inside the ear canal. This condition is called impacted cerumen.
Impacting can cause symptoms like earache, muffled hearing, itching, or a feeling of fullness in the ear. In such cases, professional removal by a doctor is the safest option to avoid damage to the ear.
Symptoms of ear wax blockage:
- Persistent ear pain or pressure
- Itching inside the ear canal
- Partial hearing loss or muffled sounds
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Dizziness or balance problems
5. Health Risks of Ignoring Ear Wax
Ignoring earwax problems can have serious consequences:
- Ear Infections & Inflammation: Bacteria thrive in trapped earwax.
- Temporary Hearing Loss: Blockages prevent sound from reaching the eardrum.
- Balance Issues & Vertigo: Impacted wax can affect the inner ear’s balance system.
- Eardrum Damage: If untreated, severe pressure may cause injury to the eardrum.
6. Unsafe Ear Cleaning Methods to Avoid
Many people damage their ears without realizing it by using unsafe methods:
- Cotton Swabs/Q-tips: Push wax deeper and risk perforating the eardrum.
- Hairpins or Sharp Objects: Can scratch the ear canal or cause bleeding.
- Ear Candles: A dangerous and ineffective practice that can lead to burns or blockages.
7. Safe and Doctor-Recommended Ways to Remove Ear Wax
Instead of unsafe DIY hacks, try safe methods approved by specialists:
- Over-the-Counter Drops: Solutions with hydrogen peroxide or glycerin soften hardened wax.
- Ear Irrigation: Gentle flushing of the ear canal with warm water.
- Microsuction or Manual Removal: Performed by an ENT doctor using special instruments.
For stubborn or recurring cases, professional cleaning is always the safest choice.
8. When to See an ENT Specialist
Not every case of earwax can be treated at home. Seek medical help if you notice:
- Severe pain or hearing loss
- Persistent ringing in the ears
- Discharge, foul smell, or bleeding
- Recurrent blockages
An ENT specialist can assess your condition and provide safe, effective treatment using advanced tools.
9. Prevention Tips for Healthy Ears
The best way to maintain ear health is through prevention:
- Don’t overclean—let your ears self-regulate.
- Avoid inserting foreign objects.
- Keep your ears dry after swimming or bathing.
- Schedule regular ENT checkups, especially if you have frequent blockages.
10. Protect Your Ears Before It’s Too Late
Earwax might seem insignificant, but it plays a vital role in maintaining your ear health. The real issue arises when it’s ignored or removed improperly. Excess wax buildup can lead to infections, discomfort, or even hearing loss. The key is balance—let your ears self-clean, avoid using cotton swabs or sharp objects, and don’t ignore early symptoms like itching or muffled hearing.
For lasting ear health, be proactive rather than reactive. Regular check-ups with an ENT specialist can prevent small issues from turning into serious ear conditions.
Expert Ear Care with Dr. Sushant Joshi at ENT FOR ALL
If you’re experiencing ear discomfort, hearing issues, or frequent earwax buildup, consult Dr. Sushant Joshi, a renowned ENT surgeon at ENT FOR ALL, the No. 1 ENT Clinic in Rajasthan. The clinic provides complete care for the Ear, Nose, and Throat, including specialized services like the Deafness Clinic, Allergy Clinic, Voice Clinic, Nose Allergy Clinic, and Ear Hospital in Udaipur.
👉 Book your consultation today at ENT FOR ALL and experience expert ENT care in Udaipur!
FAQ – Ear Wax and Ear Health
1. Is earwax harmful?
Ans. No, earwax is a natural substance that protects and lubricates the ear. It only becomes a problem when it builds up excessively or is removed incorrectly.
2. Can I use cotton swabs to clean my ears?
Ans. No. Cotton swabs push wax deeper into the ear canal and can cause blockages, irritation, or even eardrum injury.
3. How do I know if I have impacted earwax?
Ans. Signs include ear pain, itching, partial hearing loss, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), or a feeling of fullness in the ear.
4. What are safe ways to remove earwax at home?
Ans. You can use over-the-counter ear drops, gentle ear irrigation, or see a doctor for microsuction or manual removal. Avoid DIY methods like hairpins or ear candles.
5. When should I see an ENT specialist?
Ans. If you experience severe pain, persistent hearing loss, discharge, foul smell, bleeding, or recurrent blockages, consult an ENT specialist for safe treatment.